Vitamin D
CHF 69.00
Measure the levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in your blood. Vitamin D is essential for bone health, calcium and phosphorus absorption, and immune system function.
This is a pre-order product. We plan FDA 510(k) Clearance in North America and CE Mark in Europe in Q4 2024. We plan to start shipping in Q1 2025.
Capillary Blood Sample
Finger prick collection
Age 18+
15 minutes time to result
About the test
Vitamin D serves a dual role as a nutrient obtained through diet and a hormone produced by the skin in response to sunlight exposure. Its crucial involvement in bone health includes the regulation of calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for building robust bones. Additionally, Vitamin D influences nerve, muscle, and the immune system, as well as mental health.
This blood test specifically measures 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-D), providing a comprehensive assessment of your body’s stored vitamin D levels. Prolonged deficiency in Vitamin D has been associated with fatigue, bone pain, and even depression.
While natural sources of Vitamin D are limited in food, dairy and cereals can be fortified with it. In cases of low vitamin D levels, supplementation may be recommended, particularly in situations where exposure to natural sunlight is restricted. Foods rich in Vitamin D include fortified milk or plant-based alternatives, fortified breakfast cereals, and fatty fish like trout, salmon, tuna, and mackerel, as well as fish liver oils.
Who should take this test
The Vitamin D test is recommended for those with limited sun exposure, dark-skinned individuals, the elderly, people with malabsorption issues, obesity, bone health concerns, and those experiencing symptoms like fatigue or depression. Pregnant and breastfeeding women and those with limited dietary intake of Vitamin D-rich foods should also consider the test. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised to determine individual suitability and interpret results accurately.
What’s tested
The Vitamin D test measures the concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-D) in the blood. This specific form of Vitamin D provides a key indicator of the body’s overall Vitamin D status.
Signs and Symptoms
Individuals with irregular Vitamin D levels might not exhibit noticeable signs or symptoms. If symptoms do manifest, they could resemble those of other health conditions. If you’re encountering the following symptoms, it may be worth considering a Vitamin D test.
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency:
- Fatigue: persistent tiredness and lack of energy
- Bone pain: aching or pain in the bones, particularly in the back and legs
- Muscle weakness and aches
- Joint pain
- Mood changes: low mood, depression, or irritability
- Difficulty in healing wounds or infections
- Thinning of hair or hair loss
- Frequent illness: increased susceptibility to infections
- Bone disorders: in severe cases, it can lead to bone-related issues like rickets in children or osteoporosis in adults
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D Toxicity (Excessive Vitamin D):
- Nausea and vomiting: digestive issues, including constipation.
- Generalized weakness and fatigue
- Kidney problems
- Cognitive issues and confusion
- Heart arrhythmias: irregular heartbeats in severe cases
- Excessive thirst and dehydration
Eligibility
The Vitamin D Test is available for anyone over the age of 18 who wishes to measure their level and is concerned about deficiency or toxicity.
Before your Test
No special preparation is needed for this test. Fasting is not necessary.
After your Test
Your test results will be available in the 1DROP App and patient portal on the website, tablet or computer. You will receive a comprehensive and easy-to-understand report. You will be alerted if your results are outside the normal ranges.
Interpret the Results
The general guidelines are as follows:
- Deficiency: A level below 20 ng/mL is considered deficient and may require supplementation.
- Insufficiency: Levels between 20-30 ng/mL are sometimes classified as insufficient, indicating a lower-than-optimal range.
- Sufficiency: Adequate Vitamin D levels typically range between 30-50 ng/mL.
- Optimal: An optimal range for health benefits is 40-60 ng/mL.
- Excess: Levels above 100 ng/mL are considered excessive and may lead to toxicity, causing adverse effects.
HOW IT WORKS
Order online test anywhere

Choose Your Tests
Shop for tests on the 1DROP website or App. Order your tests and they will be shipped to you.
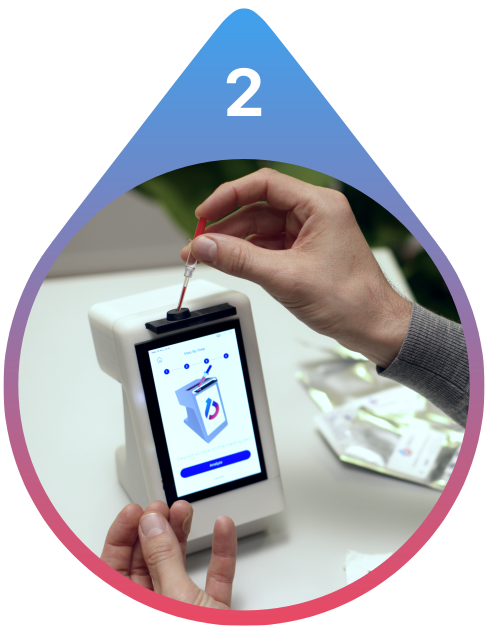

Test Your Sample
Insert the Chip into the Reader. Collect a finger prick of blood and place it on the Chip. The 1DROP Reader analyzes your sample within 15 minutes.
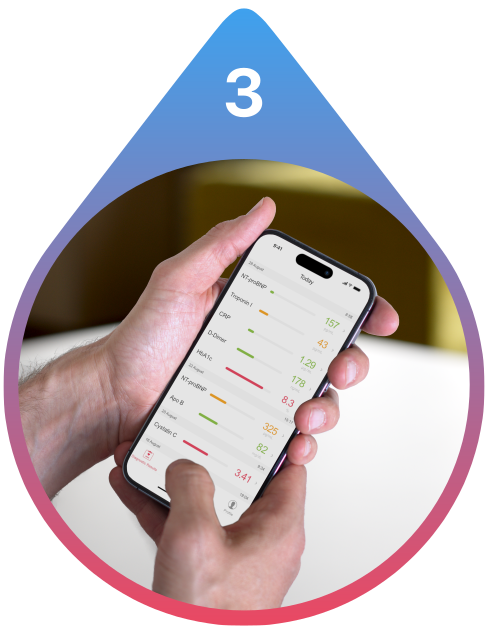

View Your Results
View your test results on the secure and private patient portal on your smartphone, tablet or computer. Easily share your results with your doctor, family, friends. Obtain guidance on your next steps.
BENEFITS
Take control of your health
Easy, rapid, affordable home testing
Convenient and Fast
Easy to Use and Understand
Personalized
Reduce Preanalytical Error
Private & Secure
Actionable Health Information
QUESTIONS
1. What causes Vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency can result from limited sun exposure, especially in individuals with darker skin tones or older adults. Inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption issues, obesity, liver or kidney disorders, and the use of sunscreen can also contribute. Geographical location and living in areas with limited sunlight play a role. Identifying these factors helps in understanding and addressing the risk of Vitamin D deficiency through measures such as increased sun exposure or supplementation. If deficiency is suspected, consulting a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance is recommended.
2. What are the risk factors for Vitamin D deficiency?
These factors contribute to the risk of Vitamin D deficiency:
- Limited sun exposure
- Darker skin tones
- Aging (especially older adults)
- Inadequate dietary intake of Vitamin D-rich foods
- Malabsorption issues (e.g., celiac disease, Crohn’s disease)
- Obesity
- Liver or kidney disorders affecting Vitamin D conversion
- Geographical location with limited sunlight
- Regular use of sunscreen
- Certain medications (e.g., anticonvulsants, glucocorticoids)
- Increased Vitamin D requirements during pregnancy and breastfeeding
3. How can I increase my Vitamin D levels?
Here are some ways to increase your Vitamin D levels
- Sun Exposure: Spend time outdoors in sunlight, especially during midday when the sun’s rays are strongest. Aim for about 10-30 minutes of sun exposure on arms, legs, face, and back, several times a week
- Dietary Sources: Include Vitamin D-rich foods in your diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and mushrooms.
- Supplements: Consider Vitamin D supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially if you have limited sun exposure or dietary intake.
- Cod Liver Oil: Cod liver oil is a natural source of Vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Fortified Foods: Such as fortified milk, orange juice, and breakfast cereals.
- UV Lamps: UV lamps or bulbs designed for Vitamin D synthesis can be used under controlled conditions, but their use should be guided by healthcare professionals.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Addressing obesity may help improve the bioavailability of Vitamin D.
- Limit Sunscreen Use: While sun protection is essential, limiting the use of sunscreen during short sun exposures can aid Vitamin D synthesis.
4. Can too much Vitamin D be harmful?
Excessive Vitamin D intake, leading to hypervitaminosis D, can be harmful. Symptoms include nausea, weakness, kidney problems, constipation, confusion, heart arrhythmias, and dehydration. It’s essential to adhere to recommended intake levels, consult with healthcare professionals before high-dose supplementation, and monitor Vitamin D levels through blood tests to avoid toxicity. Seek medical attention if toxicity is suspected.