Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
CHF 49.00
The Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test measures your average blood sugar level over the last 3 months. It is used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. If you have diabetes, it can gauge how well you control your blood sugar.
This is a pre-order product. We plan FDA 510(k) Clearance in North America and CE Mark in Europe in Q4 2024. We plan to start shipping in Q1 2025.
Capillary Blood Sample
Finger prick collection
Age 18+
10 minutes time to result
About the test
The HbA1c Test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. It measures the average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months by measuring the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
The HbA1c Test is used to monitor blood sugar control in people with diabetes. It is also used to identify people at risk for developing diabetes. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes aim for an HbA1c level of less than 7%.
Who should take this test
This test is suitable if you:
- Have type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- Have signs and symptoms of diabetes
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Are over the age of 45
- Are under the age of 45 and overweight with risk factors for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes
If your HbA1c Test Results are normal, it is recommended to repeat the test every three years. If your results indicate prediabetes, it is recommended to repeat the test every year.
If you have diabetes, it is recommended to get an HbA1c Test multiple times a year, according to your healthcare provider’s recommendation.
What’s tested
Hemoglobin, a protein that is present in red blood cells, transports oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and returns carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. When glucose enters the bloodstream, it binds to hemoglobin A1, forming Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c).
The HbA1c Test measures the amount of glucose that has attached to hemoglobin A1 in your blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that your body uses as its primary energy source and comes from the food you eat. With the help of insulin, glucose is taken up by your body’s cells to be used as energy.
If your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or your cells have trouble using insulin properly, your blood glucose level can become dangerously high, leading to diabetes. Diabetes is a serious disease that can damage your body’s organs if left uncontrolled.
The higher the level of glucose in the blood, the more glucose can attach to hemoglobin. The HbA1c measurement reflects the percentage of hemoglobin A1 that has glucose attached to it. If your HbA1c percentage is too high, it indicates that your average blood glucose level over the past 3 month has also been high. This is a concerning sign and can lead to serious health problems if not addressed.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of diabetes can be subtle or easily missed. It’s crucial to discuss your diabetes risk factors with your healthcare provider or get an HbA1c Test if you are experiencing the following symptoms:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Chronic fatigue
- Excessive hunger
- Dry mouth and eyes, blurred vision
- Sores, bruises, cuts that heal slowly
- Numbness, tingling or pain in the hands, legs or feet
- Unexplained weight loss
- Yeast infections
- Itchy skin
- Darkening/thickening of skin in certain areas
- Frequent infections
Eligibility
The HbA1c Test is available for anyone over the age of 18 who wishes to measure their average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months.
Before your Test
No special preparation is needed for this test. Fasting is not necessary.
After your Test
Your test results will be available in the 1DROP App and patient portal on the website, tablet or computer. You will receive a comprehensive and easy-to-understand report. You will be alerted if your results are outside the normal ranges.
Interpret the Results
Your HbA1c Test Results are presented as a percentage along with the reference ranges of test results considered normal, prediabetes or diabetes. Your healthcare provider will use the reference ranges, along with your overall health context, to interpret your HbA1c Test Results. The interpretation may differ depending on whether the test is being used to diagnose diabetes or to monitor diabetes that has already been diagnosed. A normal HbA1c level is below 5.7%, indicating a low risk of developing diabetes. An HbA1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% suggests prediabetes, which means you are at an increased risk of developing diabetes. An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher is considered indicative of diabetes.
HbA1c Test results can be affected by various factors, which can lead to higher or lower HbA1c levels. For example, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and high cholesterol can raise your HbA1c levels, while pregnancy, an enlarged spleen, and high vitamin E can lower them. Elevated HbA1c levels have been associated with severe health conditions, such as damage to the eyes, kidneys, heart, nerves, and blood vessels caused by high blood glucose levels. People without diabetes who have high HbA1c levels are at increased risk of metabolic disease, heart disease, and dementia.
Some metabolic health experts have more conservative recommendations, setting the maximum normal HbA1c level of 5.0% as the optimal upper limit. This underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans and regular monitoring to maintain optimal metabolic health.
| HbA1c Reference Range | |
| Normal metabolism | <5.7% |
| Prediabetes | 5.7% to 6.4% |
| Diabetes | >6.5% |
HOW IT WORKS
Order online test anywhere

Choose Your Tests
Shop for tests on the 1DROP website or App. Order your tests and they will be shipped to you.
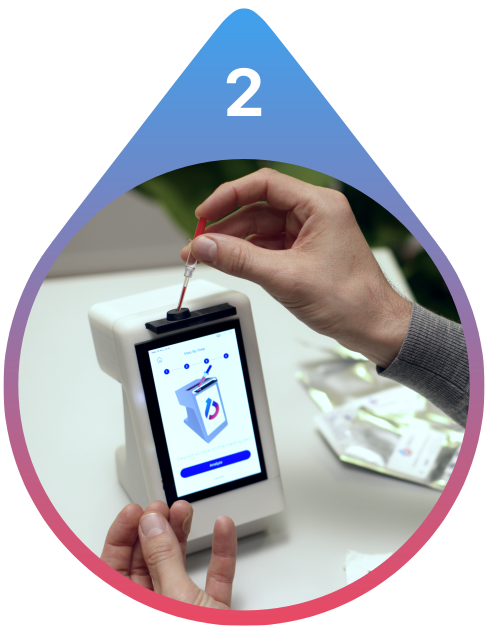

Test Your Sample
Insert the Chip into the Reader. Collect a finger prick of blood and place it on the Chip. The 1DROP Reader analyzes your sample within 15 minutes.
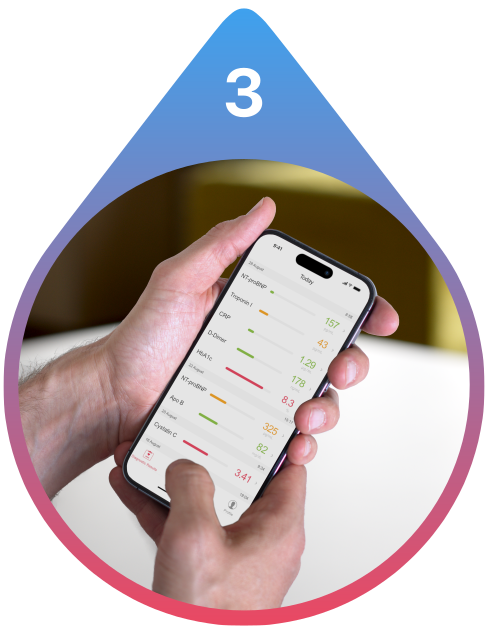

View Your Results
View your test results on the secure and private patient portal on your smartphone, tablet or computer. Easily share your results with your doctor, family, friends. Obtain guidance on your next steps.
BENEFITS
Take control of your health
Easy, rapid, affordable home testing
Convenient and Fast
Easy to Use and Understand
Personalized
Reduce Preanalytical Error
Private & Secure
Actionable Health Information
QUESTIONS
1. What's the difference between a HbA1c Test and a Blood Glucose Test?
The HbA1c Test measures the average blood sugar level over the past 3 months while the Blood Glucose Test measures the amount of glucose in the blood at a specific point in time. The HbA1c Test assesses long-term blood sugar control while the Blood Glucose Test routinely monitors blood sugar levels.
2. What does an elevated HbA1c mean?
An elevated HbA1c level indicates that your blood sugar has been high over the last 3 months. Glucose molecules attach to hemoglobin in red blood cells leading to a high percentage of HbA1c. Consistently high HbA1c levels can lead to long-term complications. People with diabetes should monitor their levels regularly and work with their healthcare team to manage their blood sugar levels.
3. What's the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas (beta cells), leading to insufficient insulin production and high blood sugar levels. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or a pump to manage their blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is commonly diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, but it can also occur in adults.
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in sugar and saturated fats. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, exercise, and dietary modifications, although medication may also be required. Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults, but it can also occur in children and adolescents.
4. What are the risk factors for type 1 diabetes?
The risk factors for type 1 diabetes include genetic susceptibility, family history of the disease, certain viral infections, and exposure to environmental factors like toxins or foods that trigger an autoimmune response. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy. The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may play a role in its development. Early diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes are important to prevent long-term complications.
5. What are the risk factors for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes?
The risk factors for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes include being overweight or obese, physical inactivity, a family history of diabetes, age (being over 45), high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a history of gestational diabetes or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanic/Latinos, Native Americans, and Pacific Islanders are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, a diet high in sugar and saturated fats, and a history of cardiovascular disease can increase the risk of developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
6. How can I lower my HbA1c?
There are various ways to decrease HbA1c levels, including making dietary changes by avoiding sugary and processed foods while increasing the consumption of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Physical activity can also help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, leading to decreased HbA1c levels. Medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to manage blood sugar levels. Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels can help identify trends and make necessary adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.