Vitamin B12
CHF 49.00
The Vitamin B12 test measures the levels of this essential nutrient in your blood. Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation. The test helps diagnose deficiencies which can lead to fatigue, weakness, and neurological issues.
This is a pre-order product. We plan FDA 510(k) Clearance in North America and CE Mark in Europe in Q4 2024. We plan to start shipping in Q1 2025.
Capillary Blood Sample
Finger prick collection
Age 18+
15 minutes time to result
About the test
The Vitamin B12 test measures the levels of Vitamin B12 in your blood. Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including the formation of red blood cells, neurological health, and DNA synthesis.
This test is essential for diagnosing Vitamin B12 deficiencies, which can result in symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, numbness or tingling in the limbs, and difficulty concentrating. A deficiency may be caused by factors like poor dietary intake, malabsorption issues, or certain medical conditions.
Interpreting the results of the Vitamin B12 test helps healthcare providers diagnose deficiencies and formulate an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment may involve dietary changes, B12 supplements, or addressing underlying causes. Regular monitoring is often recommended for individuals at risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency, such as vegetarians, older adults, or those with certain health conditions.
Who should take this test
The test is recommended for individuals who may be at risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency or those experiencing symptoms associated with low B12 levels. Here are some groups of people who might consider taking the test:
- Vegetarians and Vegans: Since Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products, individuals following a strict vegetarian or vegan diet may be at a higher risk of deficiency.
- Older Adults: As people age, the ability to absorb Vitamin B12 from food may decrease. Regular testing can help identify deficiencies early.
- Individuals with Digestive Disorders: Conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or atrophic gastritis can affect the absorption of Vitamin B12. Testing is essential for those with gastrointestinal disorders.
- Pernicious Anemia Patients: Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune condition that hampers the absorption of Vitamin B12. Regular testing is essential for managing this condition.
- Symptomatic Individuals: If you experience symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency such as fatigue, weakness, numbness, or cognitive issues, taking the test can help diagnose and address the deficiency.
- Patients on Certain Medications: Some medications, like proton pump inhibitors and certain diabetes medications, may interfere with B12 absorption.
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: Adequate B12 levels are important during pregnancy and breastfeeding for the health of both the mother and the baby.
- People with Conditions that Affect Nutrient Absorption: Certain gastrointestinal surgeries, weight loss surgeries, or conditions affecting the pancreas can impact nutrient absorption, including Vitamin B12.
What’s tested
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is a vital water-soluble vitamin crucial for red blood cell formation and neurological health. The Vitamin B12 test measures its concentration in the bloodstream, helping diagnose deficiencies. This involves analyzing a blood sample to determine if levels are within the normal range. Monitoring and addressing deficiencies are crucial for overall health, especially for those at risk.
Signs and Symptoms
Vitamin B12 deficiency can manifest in various signs and symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Anemia (pale or jaundiced skin)
- Neurological symptoms (numbness, difficulty walking)
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood changes
- Glossitis and mouth ulcers
- Vision changes
- Heart palpitations
Eligibility
The Vitamin B12 test is available for anyone over the age of 18 who wishes to assess their levels.
Before your Test
No special preparation is needed for this test. Fasting is not necessary.
After your Test
Your test results will be available in the 1DROP App and patient portal on the website, tablet or computer. You will receive a comprehensive and easy-to-understand report. You will be alerted if your results are outside the normal ranges.
Interpret the Results
The interpretation of the results of a Vitamin B12 test follow a general guideline:
- Normal Range: within 200 to 900 pg/mL.
- Deficiency: Levels below 200 pg/mL with severity categorized as mild, moderate, or severe.
- Borderline Deficiency: Levels at the lower end of the normal range of 200 pg/mL, warranting close monitoring.
- Elevated Levels: High Vitamin B12 levels are uncommon and might be associated with certain health conditions.
HOW IT WORKS
Order online test anywhere

Choose Your Tests
Shop for tests on the 1DROP website or App. Order your tests and they will be shipped to you.
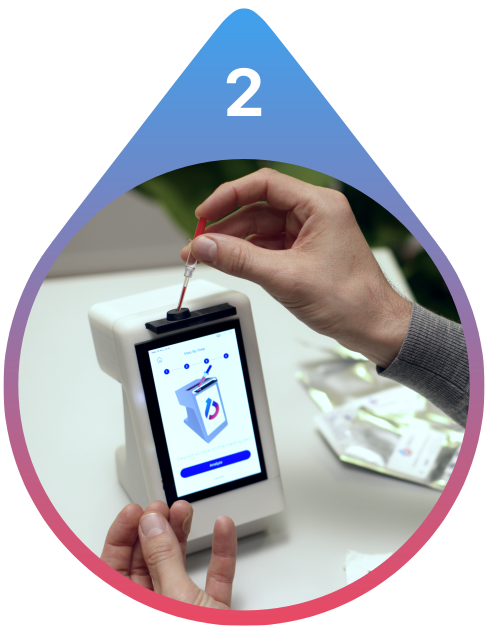

Test Your Sample
Insert the Chip into the Reader. Collect a finger prick of blood and place it on the Chip. The 1DROP Reader analyzes your sample within 15 minutes.
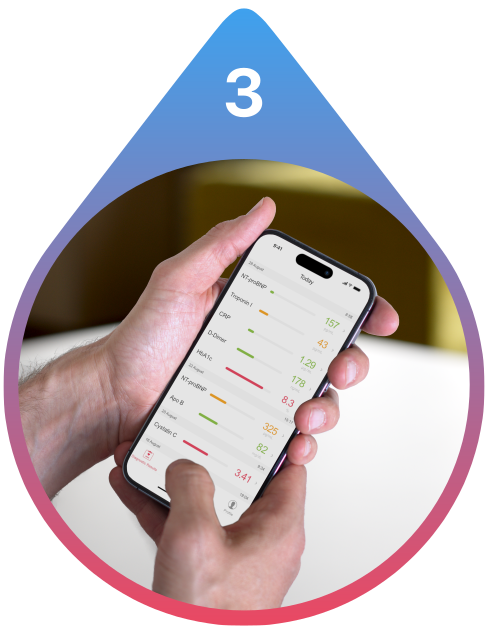

View Your Results
View your test results on the secure and private patient portal on your smartphone, tablet or computer. Easily share your results with your doctor, family, friends. Obtain guidance on your next steps.
BENEFITS
Take control of your health
Easy, rapid, affordable home testing
Convenient and Fast
Easy to Use and Understand
Personalized
Reduce Preanalytical Error
Private & Secure
Actionable Health Information
QUESTIONS
1. What causes Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by:
-
- Inadequate dietary intake, especially in strict vegetarian or vegan diets.
- Gastrointestinal disorders like celiac or Crohn’s disease.
- Pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition affecting B12 absorption.
- Aging, which can reduce B12 absorption.
- Certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and diabetes drugs.
- Gastric bypass surgery or other digestive system alterations.
- Genetic factors impacting B12 metabolism.
- Chronic use of nitrous oxide.
- Parasitic infections affecting nutrient absorption.
2. What are the risk factors for Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Risk factors for Vitamin B12 deficiency include dietary choices like strict vegetarianism, aging, gastrointestinal disorders, pernicious anemia, certain medications, gastric bypass surgery, family history, chronic use of nitrous oxide, certain health conditions, malabsorption disorders, and smoking. Identifying and addressing these factors is vital for preventing or managing B12 deficiency, and regular monitoring is recommended, particularly for at-risk individuals.
3. What is vitamin B12 deficiency anemia?
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia is a condition where insufficient Vitamin B12 impairs the normal production of red blood cells, leading to megaloblastic anemia. This deficiency affects the synthesis of DNA, particularly in rapidly dividing cells, resulting in larger and fewer red blood cells. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and neurological issues. Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause, often with dietary changes or B12 supplements. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management. If symptoms arise, consulting with a healthcare professional is advised.
4. How can I increase my Vitamin B12 levels?
To increase your Vitamin B12 levels, consider the following:
- Dietary Sources: Include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy, and fortified foods.
- Supplements: Consider B12 supplements under professional guidance.
- Intramuscular Injections: In severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend B12 injections.
- Fortified Foods: Include cereals, nutritional yeast, and fortified plant-based milk.
- Sublingual Supplements: Opt for tablets that dissolve under the tongue.
- Regular Monitoring: Undergo Vitamin B12 tests regularly if at risk.
- Address Underlying Conditions: Consult with a healthcare professional to manage any underlying conditions such as malabsorption issues, gastrointestinal disorders.
5. What are vegetarian or vegan sources of Vitamin B12?
Vegetarians and vegans can obtain Vitamin B12 from the following plant-based sources:
- Fortified Foods: Many plant-based products are fortified with Vitamin B12, including breakfast cereals, plant-based milk (soy, almond, oat, etc.), and nutritional yeast.
- Algae-Based Supplements: Some types of algae, like spirulina and chlorella, are often promoted as sources of Vitamin B12. However, their B12 content can be inconsistent, and they may contain analogs that are not effectively utilized by the human body.
- Fortified Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Certain plant-based meat substitutes may be fortified with Vitamin B12.
While these sources can contribute to Vitamin B12 intake for vegetarians and vegans, it’s important to note that B12 absorption from plant-based sources may be limited or less efficient than from animal products. Therefore, regular monitoring of B12 levels and, if necessary, supplementation under professional guidance are advisable for individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets.
6. Can too much Vitamin B12 be harmful?
In general, Vitamin B12 is considered safe, as excess is typically excreted. There’s no established upper limit. However, individual sensitivity may cause rare side effects. High doses might interact with certain medications and could mask symptoms of underlying conditions.